How to stop overclocking a CPU using Windows and BIOS settings

Table of Contents
If you were searching for how to stop overclocking a CPU, we've got everything you need to know right here.
Overclocking can be useful depending on the work you want to do, but not all CPUs are made to be overclocked, and they can't handle running on such high frequencies for extended periods. Even the ones that are made for overclocking, using them in that state for long isn’t recommended as it can reduce their lifespan.
Prime Day may have closed its doors, but that hasn't stopped great deals from landing on the web's biggest online retailer. Here are all the best last chance savings from this year's Prime event.
- Sapphire Pulse AMD Radeon™ RX 9070 XT Was $779 Now $719
- AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D Processor Was $449 Now $341
- Skytech King 95 Ryzen 7 9800X3D gaming PC Was $2,899 Now $2,599
- LG 77-Inch Class OLED C5 TV Was $3,696 Now $2,996
- AOC Laptop Computer 16GB RAM 512GB SSD Was $360.99 Now $306.84
- Lexar 2TB NM1090 w/HeatSink SSD Was $281.97 Now $214.98
- Apple Watch Series 10 GPS+ Smartwatch Was $499.99 Now $379.99
- AMD Ryzen 9 5950X processor Was $3199.99 Now $279.99
- Garmin vívoactive 5 Smartwatch Was $299.99 Now $190
*Prices and savings subject to change. Click through to get the current prices.
However, stopping your CPU from overclocking and returning it to its base clock speed can be tricky if you don't know where to look. To that end, we've put together this quick, easy-to-follow guide showing you how to change the Windows and BIOS settings to stop your CPU from overclocking.
Quick Answer
Open Settings > Power & sleep > Additional power settings > Change plan settings > Change advanced power settings > Processor power management > Change Maximum and Minimum processor state to “99%” > Click Apply and OK.
How to stop your CPU from overclocking
Long-term overclocking can lead to your CPU overheating, resulting in lowered performance and detrimental to the CPU's health. However, there are some methods that can help you to stop it from overclocking, and here's how:
Method
Change Windows power settings
Changing the Windows power settings can stop your CPU by overclocking, as you're effectively limiting how much power it consumes and its operating state.
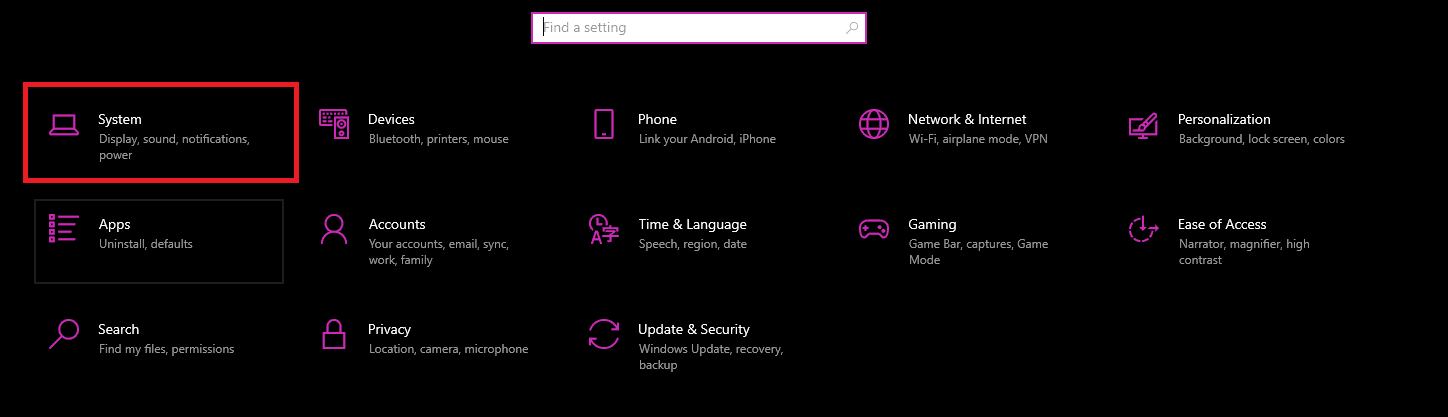
- Press “Windows Key + i” to open Settings and select “System.”
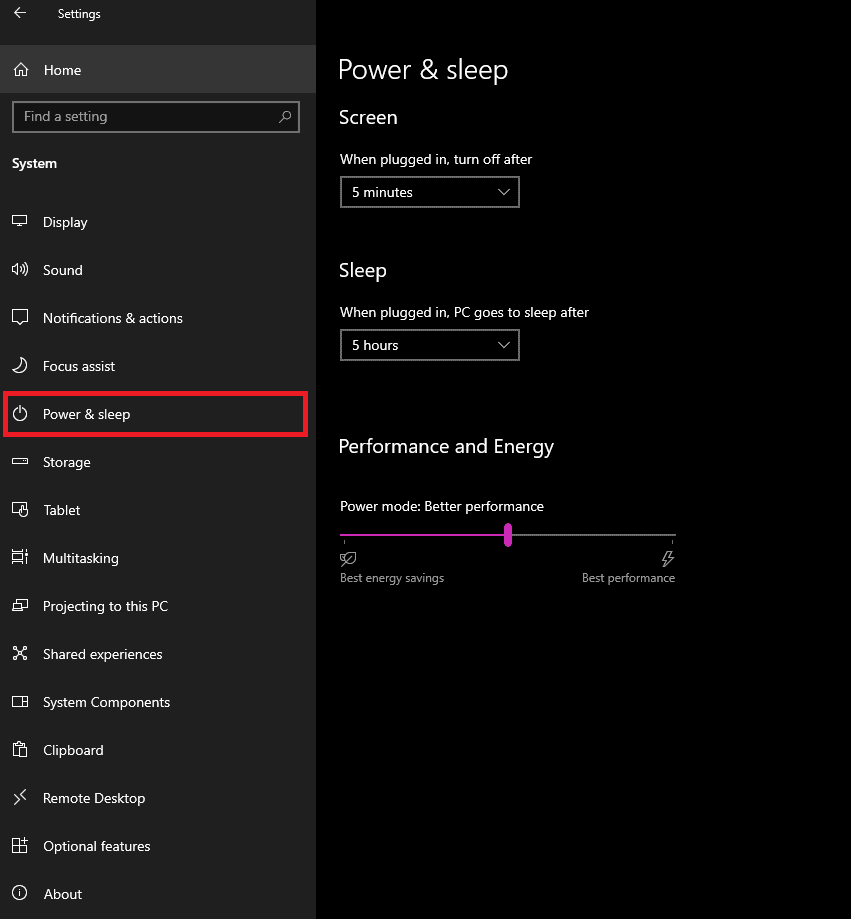
- Navigate to “Power & sleep.”
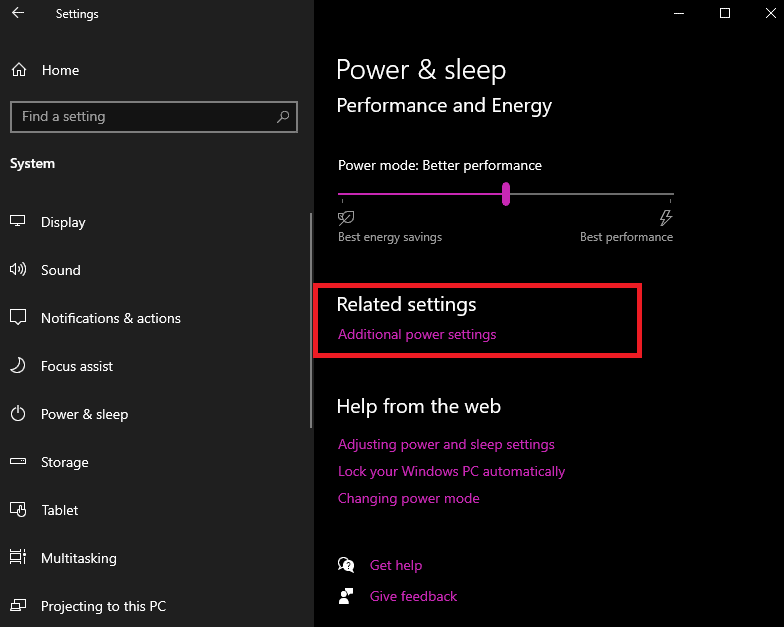
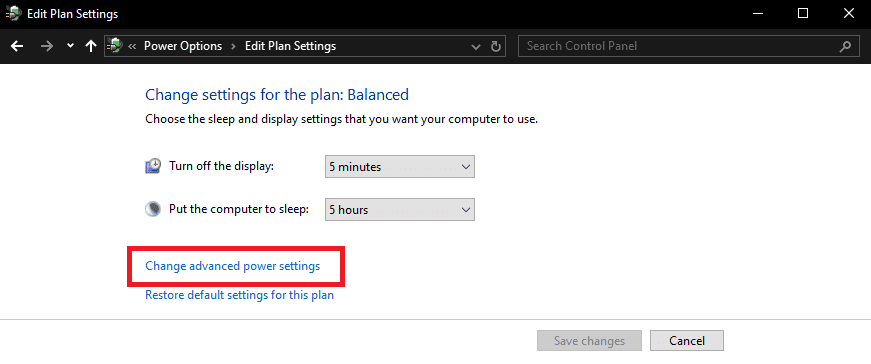
- Click on “Additional power settings.”
- This should open a new window for Power Options, where you can see the current selected power plan.
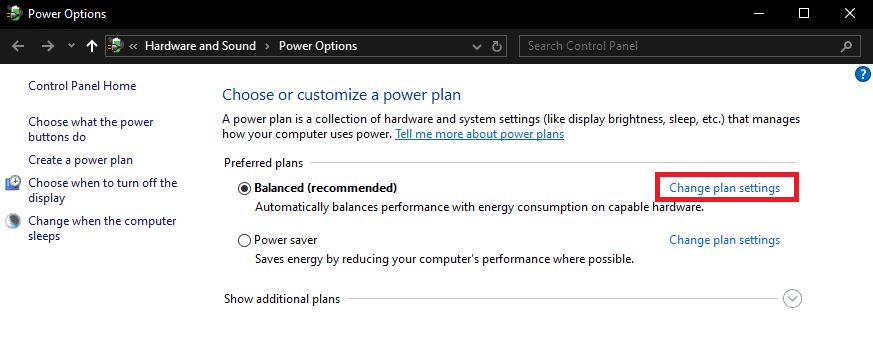
- Click on “Change plan settings.”
- Click on “Change advanced power settings.”
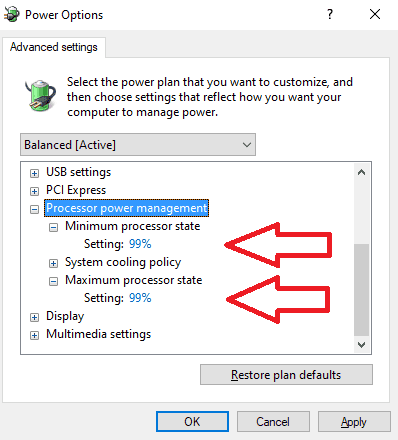
- Another window will pop up. In that window, scroll down to “Processor power management” and click on it to expand it.
- Click “Minimum processor state” and “Maximum processor state” to expand them.
- If they are set to 100%, change them to 99%, click “Apply”, and then “OK.”
This should stop your CPU from overclocking. However, if this doesn't work, give the next method a shot.
Method
Change the BIOS settings
You might be experiencing the overclocked CPU issue because the BIOS settings are configured that way. However, this is easy to fix as you only need to turn off some settings, and here is how you can do it:
- Start your PC, and as soon as you see the manufacturer logo, press “F1”, “F2”, or the “Del” key. The key varies depending on the manufacturer, so you might have to reboot your PC a couple of times to get into the BIOS.
- Once you're in the BIOS settings, navigate to the “Advanced” tab and then click on “Performance.”
- Turn off any settings that mention overclocking, core ratio boost, or turbo boost.
- Keep in mind that the terminology can vary depending on the manufacturer, so you might have to look around a bit.
- Once you've turned off those settings, save the new setting and exit the BIOS.
- Restart your PC and check if your CPU frequency has simmered down.
How do I make sure my computer isn’t overclocking?
You can ensure your CPU isn't overclocking by checking its base speed and current speed in the task manager. Open the task manager by pressing “CRTL+SHIFT+ESC,” click on the “Performance” tab, and check the “Speed” next to “Utilization” to see whether your CPU is overclocked.
You can also check the base and boost clock speed of your CPU from the manufacturer and compare it with its current speed to get an idea about whether it’s overclocking.
Wrapping up
Hopefully, this guide helped you stop your CPU from overclocking. While overclocking can be beneficial in some instances, having your CPU run beyond its capabilities for a long time can dampen its performance by overheating or thermal throttling. This also reduces the CPU’s lifespan. Luckily, there are easy workarounds for that, as we saw, that should keep your CPU running in optimal conditions.
That said, overclocking isn't the only reason processors overheat; ambient temperature, the thermal paste used, and cooling solutions can also impact that. To ensure that your processor doesn't suffer from these issues, we recommend checking out our top picks for the best thermal pastes, CPU coolers, and airflow PC cases.
After all that, if you're still running into performance issues, it might be time to swap out your CPU for a new one, and for that, we recommend these options.
-
High-end CPU
AMD Ryzen 9 7950X3D
-
Mid-range CPU
AMD Ryzen 7 5800X
- Cores: 8
- Threads: 16
- Boost clock speed: 4.7 GHz
- Base clock speed: 3.8 GHz
- L3 Cache: 32 MB
- TDP: 105 W
-
Budget CPU
Intel Core i5-13400