How to overclock a GPU – overclocking Nvidia and AMD graphics cards

Table of Contents
Overclocking a GPU or graphics card is a very straightforward task; however, you need to keep a keen eye on detail when you're doing so. The importance of the graphics card in a system is so great, although years ago you wouldn’t want to make any mistakes protections have gotten much better. So we compile a detailed guide with a step-by-step on how to overclock a GPU.
Following this process you will ensure a zero-mistake result that helps you get the advantage you need. Whether you don’t have the best graphics card and want to get extra frames on a game or finish specific video-focused tasks faster, this guide will help you accomplish that by overclocking your GPU in the safest and quickest way possible and giving you a boost even if small to your performance.
Prime Day is finally here! Find all the biggest tech and PC deals below.
- Sapphire 11348-03-20G Pulse AMD Radeon™ RX 9070 XT Was $779 Now $739
- AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D 8-Core, 16-Thread Desktop Processor Was $449 Now $341
- ASUS RTX™ 5060 OC Edition Graphics Card Was $379 Now $339
- LG 77-Inch Class OLED evo AI 4K C5 Series Smart TV Was $3,696 Now $2,796
- Intel® Core™ i7-14700K New Gaming Desktop Was $320.99 Now $274
- Lexar 2TB NM1090 w/HeatSink SSD PCIe Gen5x4 NVMe M.2 Was $281.97 Now $214.98
- Apple Watch Series 10 GPS + Cellular 42mm case Smartwatch Was $499.99 Now $379.99
- ASUS ROG Strix G16 (2025) 16" FHD, RTX 5060 gaming laptop Was $1,499.99 Now $1,274.99
- Apple iPad mini (A17 Pro): Apple Intelligence Was $499.99 Now $379.99
*Prices and savings subject to change. Click through to get the current prices.
A quick guide to overclocking
Quite simply, the quickest way to overclock is to download and install MSI Afterburner. Then once it’s going you can adjust the core and memory clock increasing them. Depending on your card it may not be possible to go all the way to the top but you can edge more and more. Each time you want to do a stress test to see if the overclock is stable.
How to overclock a GPU step-by-Step
Below we’ll go through the steps of how to overclock a graphics card, following these simple steps will give you a quick guide on how to get a bit more out of your GPU.
Step
Benchmark and stress test
Conduct a baseline performance test of your GPU. Either using the likes of the best GPU stress test tools or your favorite game, so you can get an idea of where your GPU now sits. Getting a good idea of what performance you already have on offer and how much the overclock can boost that.

Step
Download and install overclocking software
MSI Afterburner is highly recommended for its user-friendly interface and robust features. It's compatible with a wide range of GPUs and offers extensive control over clock speeds, voltage, and fan speeds. Download it from the official website and install it on your system with a simple system.

RTSS is an optional install with Afterburner that gives you a performance overlay during gaming for a quicker look at performance.
Step
Start your overclock incrementally
Begin gradually increasing your GPU's core clock speed. Start with small increments to the core clock speed, such as 20-30 MHz at a time. After adjusting the core clock, you can similarly start to increase the memory clock.
Adjusting in small increments will help in finding the optimal overclocking setting without overloading the GPU, and doing each separately makes it clear which could cause any instability. That way you can get the right combination of overclocks and get a boost.

Step
Apply and test your overclock
After each adjustment in MSI Afterburner, apply the settings. Then, run a stress test using the same tools as in Step 1. This step is crucial to ensure that the GPU remains stable and performs well under the new settings. If the GPU passes the stress test without issues (like visual artifacts, system crashes, or overheating), you can proceed to the next increment. If you encounter any instability, revert to the previous stable setting.

Step
Monitor temperature
Closely monitor the GPU temperature. As you overclock, keep a constant watch on the GPU's temperature using MSI Afterburner's real-time monitoring. It's crucial to ensure the temperature remains within a safe operating range (usually under 80-85°C, but this can vary based on the GPU model). Overheating can cause damage or reduce the lifespan of the GPU so you will want to lower your GPU temperature and keep it cool when it gets too high.

Step
Find the stable overclock and adjust fans if needed
Continue the process of incrementally increasing the clock speeds and conducting stress tests. Your goal is to find the highest clock speeds at which the GPU can run stably without any crashes, artifacts, or excessive heat. This optimal point is your stable overclock limit.
To counter the additional heat generated from overclocking, adjust the fan curve settings in the MSI Afterburner. Increase the fan speed to improve cooling, especially at higher temperatures. Effective cooling is essential to maintain the stability and longevity of the overclocked GPU. You can also leave it on automatic as Afterburner will keep the fans running well and temperatures down but you can ensure your temps are lower.
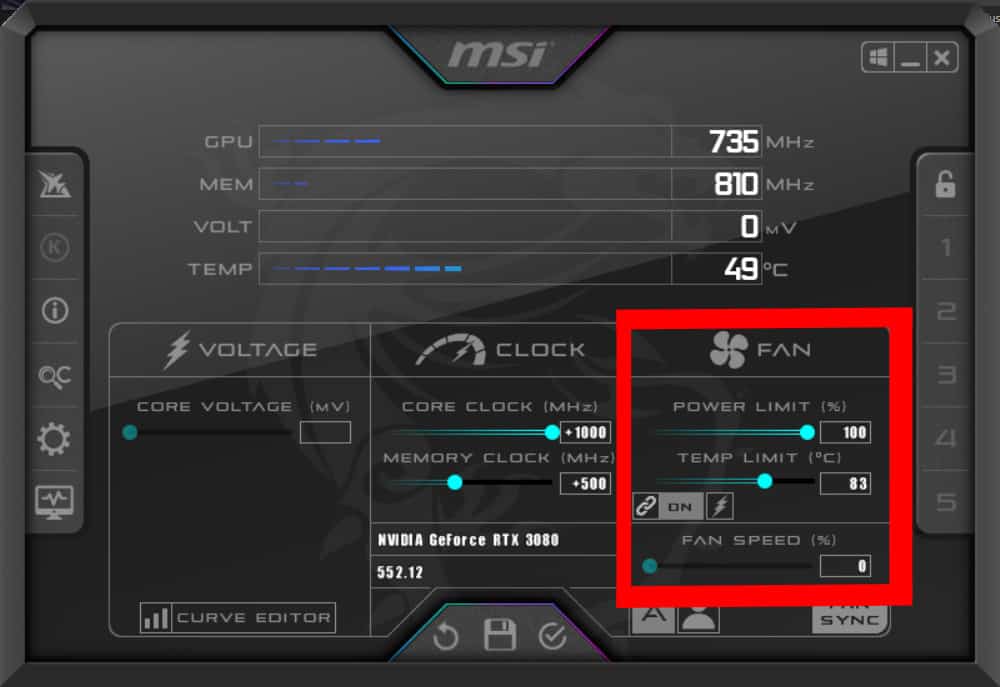
Step
Final testing
Once you've established a stable overclock, it's advisable to run extended tests to ensure the GPU's long-term stability under the new settings. Use a mix of stress tests and real-world usage scenarios, such as gaming or graphic applications, to thoroughly vet the overclock over several hours. Programs such as Furmark 2 or OCCT are good for putting real pressure on your card.

Before you overclock a GPU
Initial checks
Firstly, check you have enough power and cooling to overclock your card. You don’t want it to basically break your whole setup, or potentially overheat, making it a redundant component. If you're unsure what wattage your power supply is, you'll have to open your case and take a look. More than likely you have enough power, but there's no harm in making sure.
Another vital check is ensuring what model graphics card you have. Luckily, no need to open your case this time, you can check your system settings, or download Speccy, where you can see all of your PC's info. This will give you the knowledge to avoid any hiccups.
Update Drivers
This is a commonly overlooked step as many wouldn't think that having the correct drivers will impact overclocking. Thankfully, this is easily done both in Nvidia and AMD's proprietary control panels by simply clicking a button. You can see what drivers are currently installed and if they need updating. You can read our full guides on updating AMD graphics drivers or updating Nvidia drivers if you’re still unsure of how to do them.
Overclock performance gains
Not all overclocks can be the same, in previous generations you may have found a great deal of performance. As we saw with the Pascal GTX 10 series you could push the cards a lot more. But modern graphics don’t achieve that, or we just got unlucky with our silicon and it’s too unstable. As pushed our MSI Gaming X Trio RTX 3090 by not a significant amount, we could only get a 100MHz stable boost.
In reality, most modern cards will be towards their limits so you might not get a huge increase. As we see custom cards only improve by about 100MHz. Our Gaming X Trio already is at a 1785MHz boost over the 1695MHz factory clock, so pushing it to 1,895MHz is a good boost.
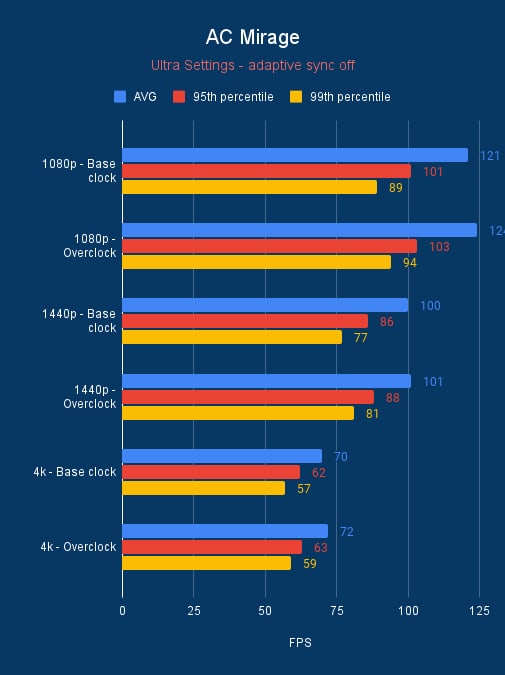
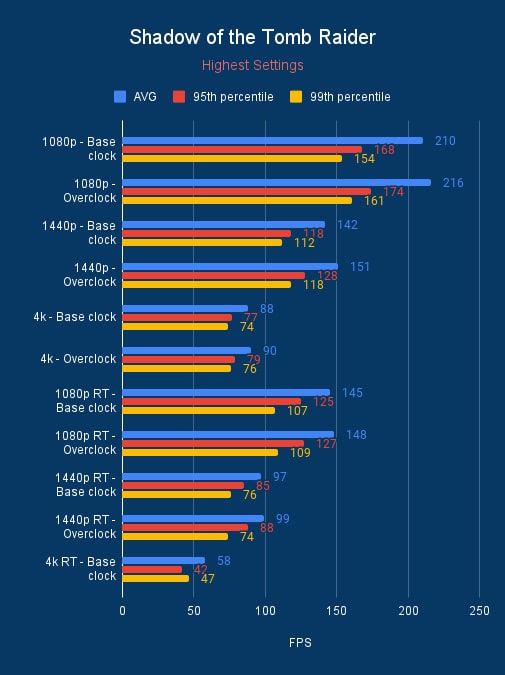
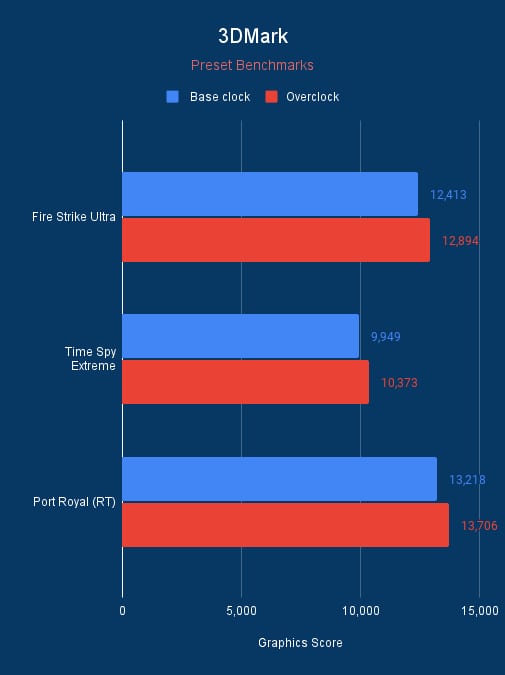
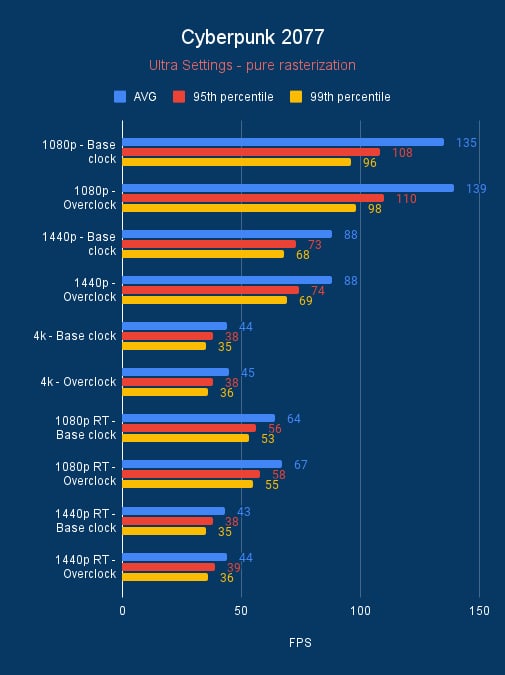
From our benchmarks, we see a slight uptick in performance, a few frames here and there in AC Mirage. Whilst Cyberpunk and Shadow of the Tomb Raider get a bit more. Although these aren’t in the tens, but 3DMark gets a good boost in the hundreds for the graphics score for each of the cards so its something.
RTX 3090 100MHz overclock vs base clock, source: BGFG
Should I overclock my GPU?
Overclocking your GPU can be a worthwhile endeavor, especially in scenarios where every bit of extra performance makes a difference. Gamers stand to gain the most immediate benefits: enhanced frame rates and smoother gameplay, particularly in graphically demanding games.
Overclocking can also extend the relevance of an older GPU, squeezing out more power and delaying the need for an expensive upgrade. For those who thrive on achieving peak system performance, the process of overclocking itself can be both challenging and rewarding, offering a deeper understanding of your hardware's capabilities.
Professionals in fields like video editing, 3D modeling, and animation, where rendering times are critical, also find substantial value in overclocking. Faster clock speeds can translate to quicker render times, enhancing overall productivity. However, it’s important to balance the pursuit of performance with the stability of your system. Overclocking should be considered if you find your current setup struggling to keep up with your requirements or if you’re looking to maximize the potential of your existing hardware.
Can I overclock my GPU on any motherboard?
Overclocking a GPU is generally independent of the motherboard used. Unlike CPU overclocking, which often requires a motherboard that supports overclocking, GPU overclocking is primarily dependent on the graphics card itself and the software used to overclock it. Most modern GPUs can be overclocked using software provided by the GPU manufacturer, so it’s more down to if you have enough power and stability to work with the overclock rather than other components.
Does overclocking reduce a GPU’s lifespan?
Overclocking a GPU can potentially reduce its lifespan, primarily due to increased operational temperatures and voltage stress. When a GPU is overclocked, it operates beyond its factory-set parameters, which can lead to higher heat output. Consistently high temperatures can accelerate wear and tear on the hardware components, especially if the cooling solution is inadequate. But adjusting your options and doing a thorough job of keeping temps down can be a good thing to do.